Climate - Land - Energy - Water nexus
Improving the way Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use sectors (AFOLU) are represented in energy models
In the face of the urgent need to address climate change and achieve carbon-neutral economies, energy system modeling plays a critical role in guiding decision-making and scenario analysis. However, the Agriculture, Forestry, and Other Land Use (AFOLU) sector has been largely neglected in existing modeling frameworks, despite its significant influence on the energy system. This proposal outlines the methodology to bridge this gap by developing a comprehensive AFOLU module for TIMES, enhancing its capabilities to support integrated long-term scenario analysis.
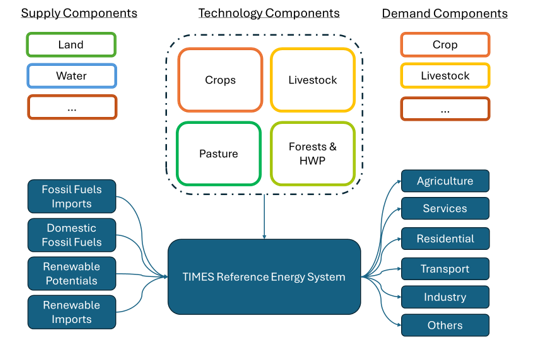 Figure 1. AFOLU sector and its interaction with energy model
Figure 1. AFOLU sector and its interaction with energy model
The AFOLU sector is central to addressing climate change impacts, significantly shaping energy system planning. Questions regarding forest capacity for CO2 uptake, optimized irrigation systems, and land allocation for biofuels production are of paramount importance. The primary methodological objective is to create a standardized, flexible AFOLU module that can seamlessly integrate with a TIMES model. This endeavor offers the ETSAP community an opportunity to enhance their models with AFOLU components and conduct more holistic scenario analysis, capturing the intricate interactions between the energy system and the AFOLU sector.
Water
Water and energy are intertwined. Energy, especially electricity, is vital for withdrawal, treating and delivering water to the end-users. On the other hand, several processes and technologies involved in the water supply chain present some of the most urban energy-intensive processes [1]. Moreover, climate change is severely affecting both water and energy resources and their supply [2], [3].
These interdependencies of water and energy resources brought us to the development of an integrated approach within TEMOA. To this end, the Pantelleria-island energy model[4] was used to develop the methodology of water-energy integration.
The implementation steps can be listed as follows:
- Development of the Reference Water System (RWS) (analogue to Reference Energy System (RES).
- Identification of the technologies in both modules which consume and produce water and/or energy commodities.
- Connect the technologies through proper parameters such as efficiency, capacity factor, activity etc.
It is important noting that despite their energy intensity [5], water system specific technologies such as water pipelines or water and wastewater treatment plants are normally missing in the energy system technology inventories. Water pipelines and wastewater treatment plant of the island were characterized within the integrated model. The following picture represents the connected water and energy systems of the Pantelleria case study.
Moreover, the incorporation of two commodities (i.e., water and energy) enables the attribution of proper drivers to each of them and consequently better projection of their evolution in long term modeling framework.
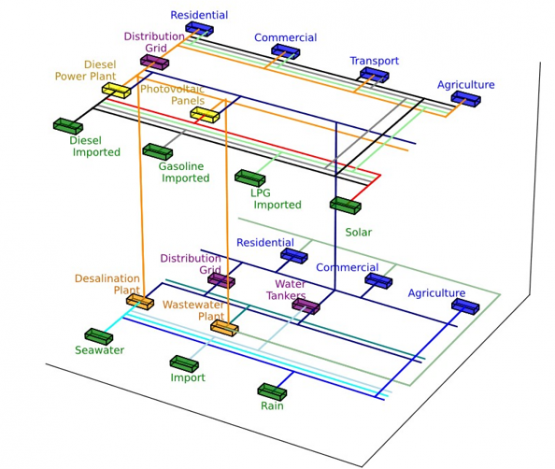
Figure 2. Pantelleria Island integrated water-energy systems
References
- N. Carter, “Energy-Water Nexus: The Water Sector’s Energy Use Claudia Copeland Specialist in Resources and Environmental Policy,” 2017, Accessed: Sep. 01, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://sgp.fas.org/crs/misc/R43200.pdf
- UN Water, “Water and Climate Change.” Accessed: Sep. 17, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.unwater.org/water-facts/water-and-climate-change
- W. Rosińska, J. Jurasz, K. Przestrzelska, K. Wartalska, and B. Kaźmierczak, “Climate change’s ripple effect on water supply systems and the water-energy nexus – A review,” Water Resour Ind, vol. 32, p. 100266, Dec. 2024, doi: 10.1016/J.WRI.2024.100266.
- M. E. Alfano, “Modeling the Energy and the Water Systems in an open-access Energy System Optimization Model: the Pantelleria case study,” Politecnico di Torino, 2022. Accessed: Jan. 19, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://webthesis.biblio.polito.it/24982/
- N. Carter, “Energy-Water Nexus: The Water Sector’s Energy Use Claudia Copeland Specialist in Resources and Environmental Policy,” 2017, Accessed: Sep. 01, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://sgp.fas.org/crs/misc/R43200.pdf

